How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Easy Hacks for Beautiful and Healthy Roses – the allure of these fragrant blooms is undeniable. Growing roses from cuttings is a rewarding and accessible way to expand your garden, and with the right techniques, even beginners can achieve success.
From choosing the right cuttings to nurturing them into thriving plants, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for cultivating healthy and beautiful roses.
This article explores the art of rose propagation, taking you step-by-step through the process. We’ll cover everything from selecting the ideal cuttings to providing the perfect rooting environment. With a little patience and care, you can enjoy the beauty and fragrance of roses propagated from your own garden.
The Allure of Rose Propagation
Roses, with their exquisite beauty and intoxicating fragrance, have captivated hearts for centuries. Their cultivation, however, can be a demanding endeavor. Yet, there’s a magical secret to unlocking a garden brimming with these cherished blooms: rose propagation. This technique allows you to create new rose plants from existing ones, transforming your gardening journey into a rewarding and fulfilling experience.
Benefits of Propagating Roses From Cuttings
Rose propagation from cuttings offers a multitude of advantages, making it a highly desirable method for rose enthusiasts:
- Cost-Effectiveness:Propagating roses from cuttings is a budget-friendly approach. It eliminates the need to purchase new plants, saving you significant expenses.
- Preservation of Desired Traits:This method ensures the preservation of the unique characteristics of your beloved rose varieties. Whether it’s a vibrant color, a distinctive fragrance, or a specific flower form, you can replicate these traits in your new plants.
- Genetic Continuity:By propagating from cuttings, you maintain the genetic integrity of the parent plant, ensuring that the new roses inherit its desirable qualities.
- Increased Variety:Rose propagation opens doors to expanding your garden’s diversity. You can experiment with different varieties, creating a vibrant and visually appealing landscape.
- Enhanced Garden Design:The ability to propagate roses allows you to create specific arrangements and designs within your garden. You can strategically place roses where they thrive, maximizing their beauty and impact.
Advantages of Cuttings Over Other Propagation Methods
Rose propagation from cuttings offers distinct advantages over other techniques, such as grafting or budding:
- Simplicity:Cuttings are generally easier to propagate than other methods. They require less specialized knowledge and equipment, making them accessible to novice gardeners.
- Faster Growth:Rose cuttings typically root and grow faster than grafted or budded roses. This allows you to enjoy blooms sooner, adding a touch of beauty to your garden more quickly.
- Disease Resistance:Roses propagated from cuttings are often more resistant to diseases than those grown from other methods. This is because cuttings are genetically identical to the parent plant, inheriting its disease resistance.
- Greater Success Rate:With proper technique and care, rose propagation from cuttings has a high success rate, ensuring a bountiful harvest of new rose plants.
Why Rose Propagation is a Rewarding Gardening Practice
Rose propagation is not merely a technique; it’s a rewarding and enriching gardening experience. The process of nurturing a cutting from its initial stages to a flourishing rose plant is deeply satisfying:
- Sense of Accomplishment:Watching a tiny cutting transform into a vibrant rose plant instills a sense of pride and accomplishment. You’ve played an active role in creating something beautiful and unique.
- Connection to Nature:Rose propagation fosters a deeper connection to the natural world. You become actively involved in the cycle of life, witnessing the growth and development of a new plant.
- Creative Expression:Rose propagation allows you to express your creativity. You can experiment with different varieties, create unique arrangements, and personalize your garden to reflect your individual style.
- Sharing the Joy:Propagating roses allows you to share your passion with others. You can gift cuttings to friends and family, spreading the beauty and joy of roses.
Choosing the Right Cuttings
Selecting the right rose cuttings is crucial for successful propagation. Understanding the ideal time for taking cuttings and identifying healthy stems will significantly increase your chances of success.
Ideal Time for Taking Rose Cuttings
The best time to take rose cuttings is during the dormant season, typically from late fall to early spring, when the plant is not actively growing. This period allows the cuttings to focus their energy on root development rather than leaf growth.
During this time, the plant’s sap flow is reduced, which helps prevent wilting and promotes root formation.
Characteristics of Healthy Rose Stems
Healthy rose stems suitable for propagation exhibit specific characteristics:* Mature Stems:Choose stems that are mature and woody, typically from the current year’s growth. These stems are strong enough to support root development.
Disease-Free
Ensure the stems are free from any signs of disease or pest damage, such as spots, discoloration, or insect infestations. Healthy stems will produce healthy roots.
Vigorous Growth
Look for stems that have shown vigorous growth, indicating their ability to produce strong roots.
Selecting the Best Rose Cuttings
To select the best rose cuttings for propagation, follow these steps:
- Choose a Healthy Rose Bush:Select a healthy rose bush that is free from disease and has vigorous growth.
- Identify a Mature Stem:Look for a stem that is mature and woody, typically from the current year’s growth.
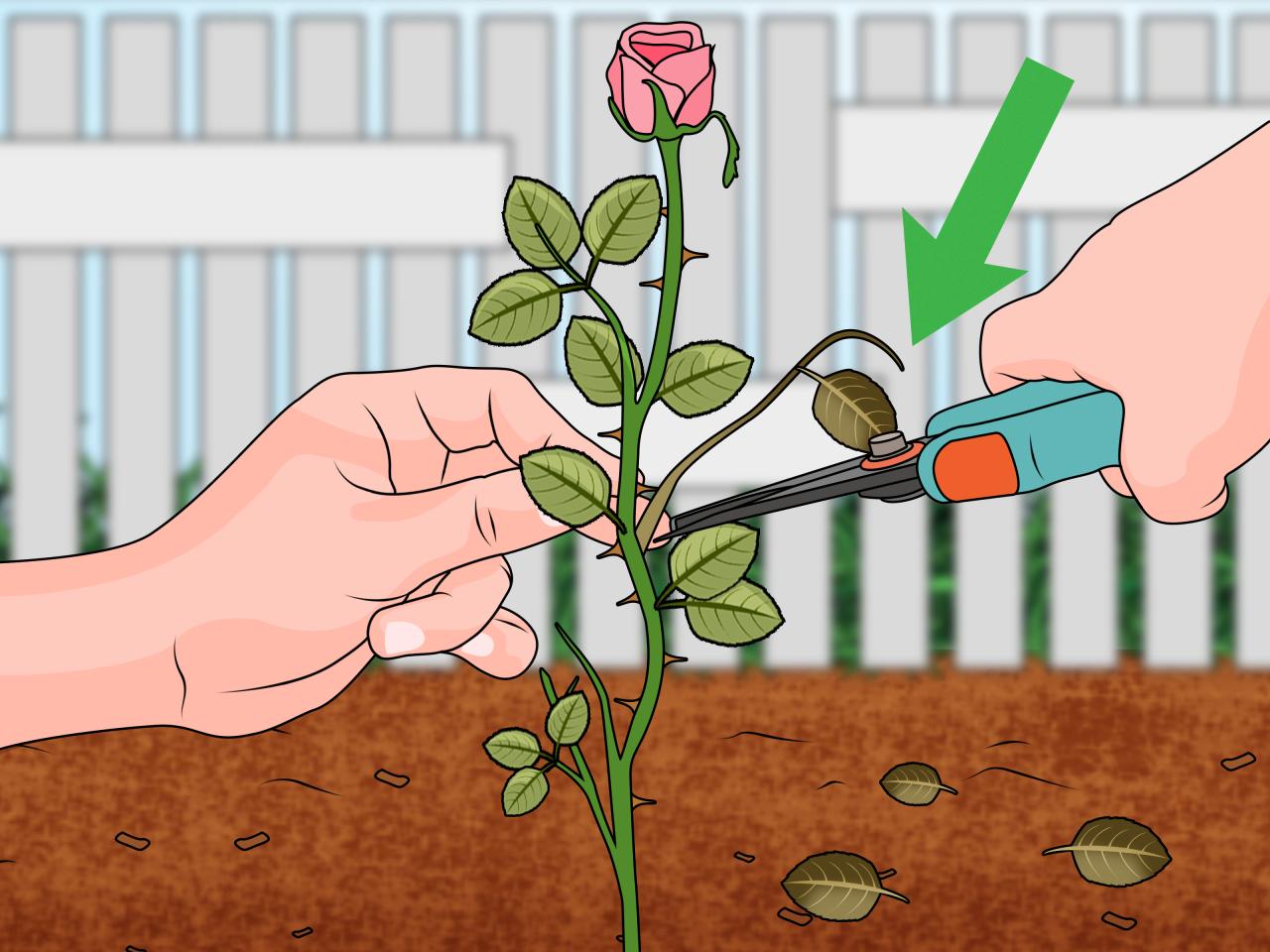
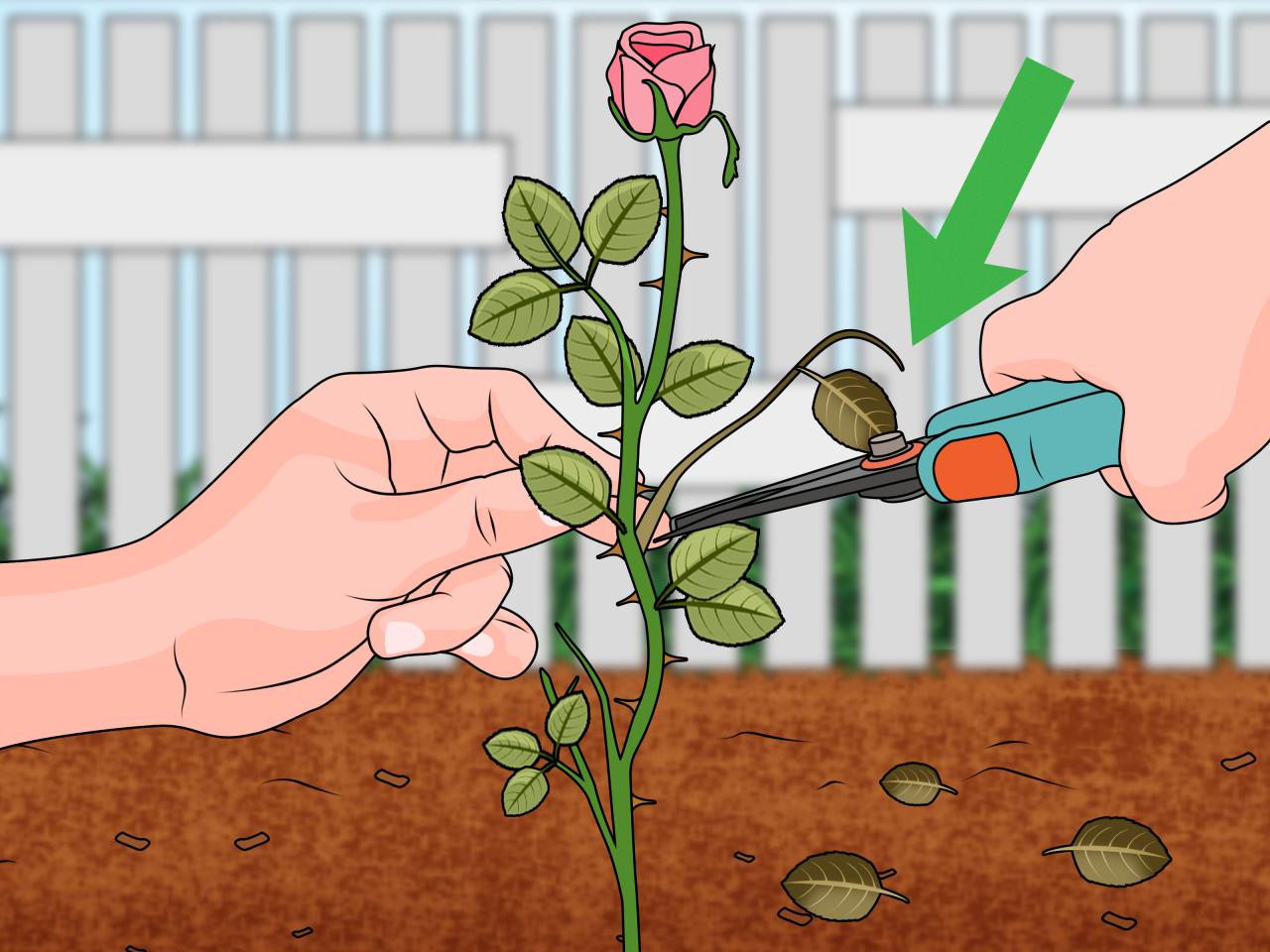
- Cut the Stem:Using clean, sharp pruning shears, cut the stem at a 45-degree angle just below a node (where a leaf or bud grows).
- Remove Leaves:Remove all leaves from the bottom 2-3 inches of the stem, leaving only a few leaves at the top.
- Prepare the Cutting:Dip the cut end of the stem in rooting hormone powder to encourage root growth.
- Plant the Cutting:Plant the cutting in a well-draining potting mix, ensuring that the bottom 2-3 inches are buried in the soil.
Preparing the Cuttings
Once you’ve chosen the perfect rose stems for propagation, it’s time to prepare them for their transformation into new plants. This step is crucial for maximizing success and ensuring healthy growth.Proper preparation involves making precise cuts, removing unnecessary parts, and creating an environment conducive to root development.
Making Clean Cuts
Making clean cuts is essential for preventing infections and promoting root growth. Sharp tools, such as pruning shears or a sharp knife, are crucial for this task.
- Use a clean, sharp blade to make a diagonal cut at the base of the cutting, just below a node (the point where a leaf or branch grows). This angled cut increases the surface area for root development.
- Make a straight cut at the top of the cutting, just above a leaf node. This ensures that the cutting has enough energy to focus on root growth.
Removing Leaves and Thorns
Removing leaves and thorns from the lower portion of the cutting is essential for two reasons:
- It prevents the leaves from losing moisture and energy that is needed for root development.
- It reduces the risk of fungal infections, which can thrive in moist, shaded areas.
Rooting Methods
Once you have prepared your rose cuttings, it’s time to choose a rooting method. There are two main approaches: water propagation and soil propagation. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice for you will depend on your individual preferences and resources.
Comparison of Rooting Methods
The following table provides a comprehensive comparison of the two main rooting methods, outlining their advantages and disadvantages.
Rooting Method |
Description |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
Water Propagation |
This method involves placing the cuttings in a container of water and allowing the roots to develop. |
|
|
Soil Propagation |
This method involves planting the cuttings directly in a suitable rooting medium, such as a mix of potting soil and perlite. |
|
|
Water Propagation
This method involves placing the prepared cuttings in a container of water, ensuring that the nodes are submerged. It’s crucial to change the water every few days to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi. As the roots develop, you can gradually increase the depth of the water.
Once the roots are about 2-3 inches long, the cuttings can be transplanted into soil.
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding way to expand your garden, but it can also be a great way to create a unique and miniature version of your favorite rose varieties. If you’re looking for a more compact and manageable approach, consider exploring the art of Bonsai , which allows you to cultivate miniature trees, including roses, in stunning and controlled forms.
This ancient practice offers a fascinating parallel to rose propagation, as both involve careful pruning and shaping to achieve a desired aesthetic.
Soil Propagation
For soil propagation, you’ll need a suitable rooting medium, such as a mix of potting soil and perlite. Fill a container with the rooting medium, make a hole with a pencil, and insert the prepared cutting, ensuring that the nodes are below the soil level.
You can then cover the container with a plastic dome or bag to create a humid environment, which promotes root development. Keep the rooting medium moist but not soggy, and avoid direct sunlight. Once the roots are established, you can gradually acclimate the cuttings to outdoor conditions before transplanting them into their final location.
Creating the Ideal Rooting Environment
Rose cuttings require specific environmental conditions to develop healthy roots. Maintaining optimal humidity and temperature levels is crucial for successful propagation. A humid environment encourages root growth while warmth stimulates cellular activity.
Creating a Mini-Greenhouse
A mini-greenhouse provides the ideal environment for rooting rose cuttings. This controlled environment allows for precise humidity and temperature regulation, promoting optimal root development.
- Use a clear plastic container or a propagation dome.These structures trap moisture and create a warm, humid environment.
- Fill the container with a rooting medium.A mixture of peat moss and perlite, or a specialized rooting mix, provides good drainage and aeration.
- Place the cuttings in the rooting medium.Ensure the cuttings are firmly planted and the base is covered with the rooting medium.
- Mist the cuttings daily.This helps maintain high humidity levels, essential for root development.
- Position the mini-greenhouse in a bright location.Indirect sunlight is ideal, avoiding direct sunlight that can scorch the cuttings.
Using a Propagation Dome
Propagation domes are readily available and provide a similar environment to a mini-greenhouse. They are designed specifically for rooting cuttings and offer a more controlled environment.
- Choose a dome that is the appropriate size for your cuttings.The dome should fit snugly over the container, creating a sealed environment.
- Place the cuttings in the container and cover them with the dome.The dome will trap moisture and heat, creating a humid environment.
- Mist the cuttings regularly.This will help maintain high humidity levels and prevent the cuttings from drying out.
- Position the dome in a bright location.Indirect sunlight is ideal, avoiding direct sunlight that can scorch the cuttings.
Protecting Cuttings from Direct Sunlight and Excessive Heat
Direct sunlight can scorch cuttings, causing them to wilt and die. Excessive heat can also inhibit root development.
- Position the mini-greenhouse or propagation dome in a bright location but avoid direct sunlight.A south-facing window with a sheer curtain can provide filtered light.
- Monitor the temperature of the environment.Ideal temperatures for root development are between 65°F and 75°F (18°C and 24°C).
- If the temperature is too high, move the cuttings to a cooler location.You can also use a fan to circulate air and reduce heat buildup.
Caring for Your Rose Cuttings
Once you’ve successfully rooted your rose cuttings, it’s crucial to provide the right care to ensure their healthy development. This involves maintaining a suitable environment and providing adequate water, light, and nutrients.
Care Requirements at Different Stages of Rooting
The care requirements for rose cuttings vary depending on the stage of rooting. Here’s a table summarizing the key aspects:
Stage of Rooting |
Watering Needs |
Light Requirements |
Other Care Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
Initial Rooting (First 2-3 Weeks) |
Keep the rooting medium consistently moist, but not soggy. |
Indirect, bright light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the cuttings. |
Maintain a warm environment (around 70-75°F) for optimal root development. |
Active Root Growth (3-6 Weeks) |
Water when the top inch of the rooting medium feels dry. |
Gradually increase light exposure, acclimating the cuttings to brighter conditions. |
Monitor for signs of pests and diseases, treating promptly if necessary. |
Established Roots (6+ Weeks) |
Water regularly, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. |
Full sun, but gradually acclimate the cuttings to avoid sunburn. |
Start fertilizing with a balanced fertilizer, diluted to half strength. |
Signs of Successful Rooting
Several signs indicate successful rooting in rose cuttings. These include:
- New Growth:The emergence of fresh leaves or shoots from the cutting is a strong indicator of successful rooting.
- Firm Stem:The base of the cutting should feel firm and sturdy, indicating the development of roots.
- Resistance to Pulling:Gently tugging on the cutting should result in resistance, suggesting that the roots are anchoring the cutting.
Potential Problems to Watch Out For
While rooting rose cuttings is generally straightforward, certain problems can arise. Be on the lookout for:
- Root Rot:Overwatering or poorly draining rooting medium can lead to root rot, characterized by wilting, yellowing leaves, and a foul odor.
- Fungal Infections:Damp conditions can promote fungal infections, resulting in leaf spots, mold, or stem rot.
- Pests:Rose cuttings can be susceptible to pests like aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs.
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding way to expand your garden and enjoy these beautiful blooms. While roses can be a bit more challenging to propagate than some other plants, there are several techniques that can increase your success rate.
For a similar approach with another popular vine, check out How to Make Clematis Propagation Easy and Effective. Once you’ve mastered these methods, you’ll be well on your way to creating a stunning rose garden filled with healthy, thriving plants.
Transplanting Your Rooted Roses: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Easy Hacks For Beautiful And Healthy Roses
After months of nurturing your rose cuttings, they are finally ready to be transplanted into their permanent location. This step is crucial for their continued growth and flourishing. Proper transplanting ensures the roses have adequate space and resources to thrive, ultimately leading to a beautiful and healthy rose garden.
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. Similar to roses, schefflera plants can also be easily propagated from cuttings, offering a simple way to multiply your collection. If you’re interested in learning more about this process, check out The Complete Guide to Growing New Schefflera Plants from Cuttings.
Once you’ve mastered the art of propagating schefflera, you’ll be well on your way to successfully growing your own beautiful rose bushes from cuttings.
The Best Time to Transplant Roses
The ideal time to transplant roses is during the springor fall. This is because the weather is mild, and the roses are either actively growing or preparing for dormancy.
- Spring:Transplanting in spring allows the roses to establish themselves before the heat of summer arrives. This is a good choice for areas with hot summers.
- Fall:Transplanting in fall allows the roses to settle in before winter dormancy. This is a good choice for areas with mild winters.
Preparing the Soil for Transplanting
The soil plays a vital role in the success of your rose transplants. Prepare the soil thoroughly to ensure optimal growth and health for your roses.
- Choose the Right Location:Select a spot in your garden that receives at least 6 hours of sunlight daily. Avoid areas with poor drainage, as roses are susceptible to root rot.
- Amend the Soil:Roses prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. Amend the soil with compost, aged manure, or other organic matter to improve its structure and fertility.
- Dig a Planting Hole:Dig a hole that is twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of the rose cutting. This will allow the roots to spread out and establish themselves.
Supporting Your Newly Planted Roses
Once the rose cutting is transplanted, provide it with the necessary support to help it stand upright and grow strong.
- Stake the Rose:Use a sturdy stake to support the rose cutting, especially if it is tall or has a tendency to flop over. Tie the rose cutting to the stake loosely with soft twine or garden tape.
- Mulch Around the Rose:Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of the rose cutting. Mulch helps to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Easy Hacks for Healthy Roses
Once your rose cuttings have successfully rooted, it’s time to nurture them into thriving plants. This involves providing the right conditions for healthy growth, including proper fertilization, pest control, and pruning techniques. These simple yet effective hacks will ensure your newly propagated roses flourish and reward you with an abundance of beautiful blooms.
Fertilizing for Robust Growth
Roses are heavy feeders and require regular fertilization to thrive. Newly propagated roses, in particular, benefit from a balanced fertilizer rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which promotes strong root development, healthy foliage, and abundant blooms. A slow-release fertilizer applied at the base of the plant every few weeks is an effective option.
- Organic Fertilizers:Compost, manure, and fish emulsion are natural and sustainable options that provide essential nutrients while improving soil structure.
- Synthetic Fertilizers:Balanced fertilizers with an NPK ratio of 10-10-10 or 20-20-20 are readily available and provide a consistent supply of nutrients.
Protecting Against Pests and Diseases, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Easy Hacks for Beautiful and Healthy Roses
Roses are susceptible to various pests and diseases, which can weaken their growth and affect their overall health. Early detection and prevention are crucial for maintaining healthy roses.
- Regular Inspection:Regularly inspect your roses for signs of pests and diseases, such as aphids, spider mites, black spot, or powdery mildew.
- Organic Pest Control:Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings to naturally control pests. Neem oil or insecticidal soap can also be used to target specific pests.
- Disease Prevention:Water your roses at the base to avoid wetting the foliage, which can encourage fungal diseases. Remove any infected leaves or stems promptly to prevent the spread of disease.
Pruning for Optimal Growth and Beauty
Pruning is an essential part of rose care, as it encourages healthy growth, promotes flowering, and maintains the desired shape of the plant.
- Deadheading:Regularly remove spent blooms to encourage the production of new buds and flowers.
- Shape and Size:Prune roses in late winter or early spring to remove dead or diseased branches and to shape the plant. This helps maintain the desired size and form of the rose.
- Thinning:Remove any crossing or weak branches to allow air circulation and prevent disease.
Concluding Remarks
Propagating roses from cuttings is a fulfilling gardening experience that allows you to share the beauty of these beloved flowers with others. By following the techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can cultivate a thriving rose garden filled with vibrant blooms.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, the joy of growing roses from cuttings is a rewarding journey.
FAQ Overview
Can I propagate roses from any rose variety?
While most rose varieties can be propagated from cuttings, some are easier to root than others. Hybrid tea roses and floribunda roses are generally good choices for beginners.
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
Rooting time can vary depending on the variety of rose, the rooting method, and environmental conditions. It typically takes 4 to 8 weeks for cuttings to develop roots.
What should I do if my rose cuttings are wilting?
Wilting is a sign of dehydration. Ensure the cuttings are kept moist, but not soggy. You can also mist the cuttings regularly to increase humidity.
Can I propagate roses from store-bought roses?
Yes, you can propagate roses from store-bought roses, but it’s best to choose roses that are not grafted. Look for roses that have a single stem with a bud at the top.